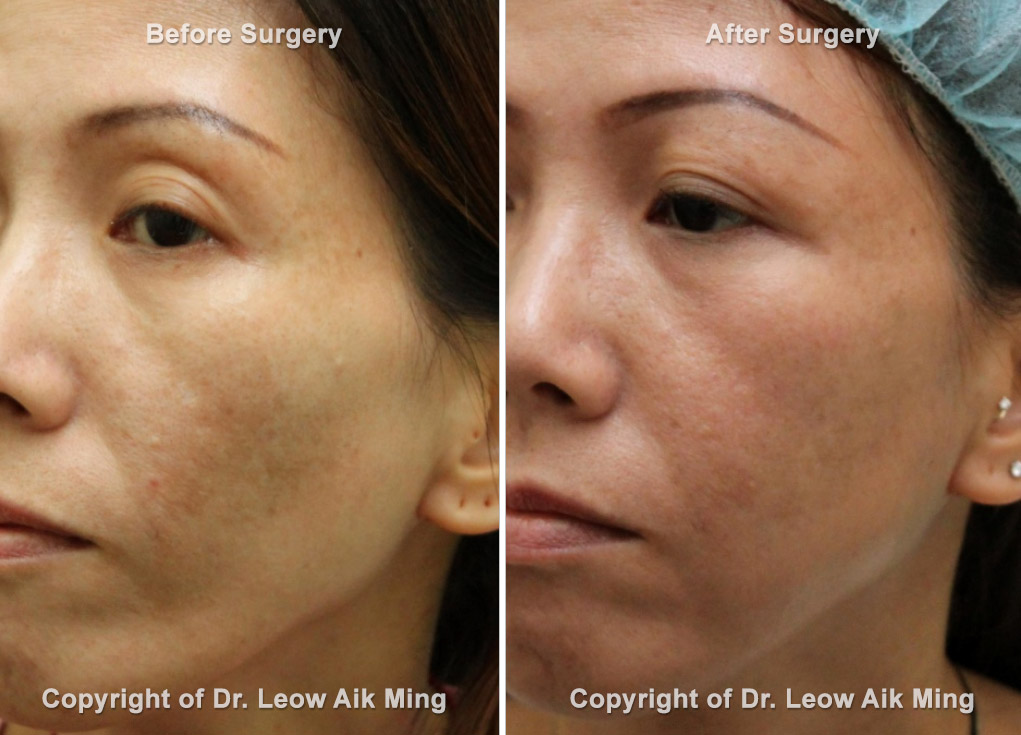
Fat grafting or lipofilling is a procedure involves in transferring fat from the areas of excess fat or undesirable areas, such as the abdomen or outer thighs, and injects it into areas that may be lacking in volume, such as the face, hands, breasts or buttocks of the same individual. Fat grafting can also be performed as a complement to traditional lifting techniques. Fat grafting alone is not sufficient to remediate the ageing process of the face.
Aesthetic indications for small volume fat grafting can be applied for facial areas that appear creased and hollow such as sunken cheeks, temporal regions or upper eyelids, deep grooves between the nose and the corners of the mouth (nasolabial fold) or lower eyelids. It is also one of the most common methods used for lip enhancement. Besides, fat grafting can also be used to smooth out all types of irregularities such as those resulting from poorly performed liposuction or injuries. On the other hand, large volume fat grafting can be used for hands rejuvenation and breasts or buttocks augmentation.
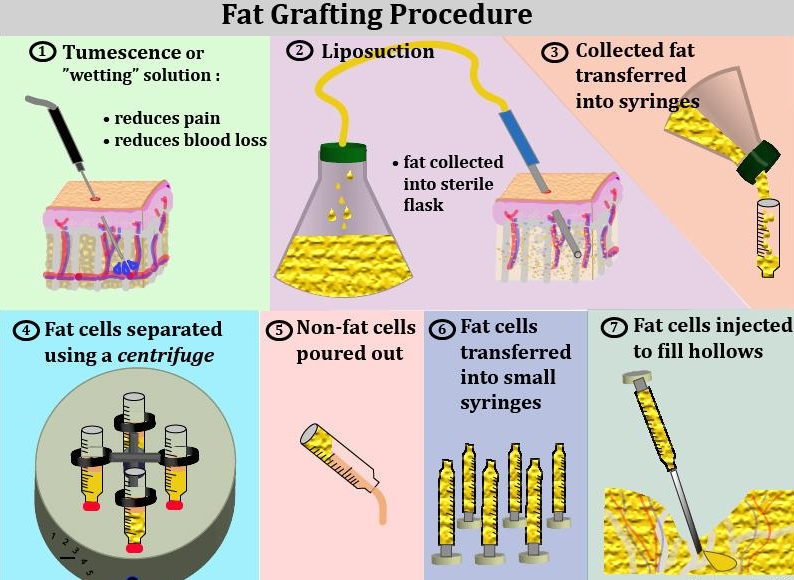
Depending upon the volume of fat harvested, treatment for target areas and patient’s preference, fat grafting can be performed either under local or general anaesthesia. Fat grafting involves three main stages:
- Fat Harvesting. Small incisions are made in the skin, and a thin cannula is used to suck out the fat (similar to liposuction). The incisions are then closed with stitches and a small dressing placed over them (Diagram No.1-3).
- Fat Preparation. Special equipment (centrifuge) is used to quickly spin the fat, to separate it from any blood and other fluids (Diagram No.4-6).
- Fat Injection. A needle and syringe are used to inject small amounts of fat into the treatment area. Fine needles are usually used to inject the fat. Hence stitches are not often needed (Diagram No.7).
Advantages of fat grafting include using your fat cells rather than foreign body injectables, the transferred fat will last longer than injectable fillers, besides improving the volume it also enhances blood circulation to the treated areas and produces natural-looking aesthetic results.
Ideal candidates for fat grafting
- Healthy individuals who do not have a life-threatening illness or medical conditions
- Individuals who are motivated and have realistic expectations
Preoperative evaluation for fat grafting
Communication is vital to achieving the patient’s goals. During the initial consultation, patients will have the opportunity to discuss their goals and desired results with the plastic surgeon. The plastic surgeon will work closely with the patients to reach an agreement about the expectations from the surgical procedures involved and their long term benefits. Every patient is different. Therefore a specific treatment regimen is planned to suit an individual’s need.
The preoperative evaluation for fat grafting includes:
- Discussion about patients’ expectations and desired outcome
- Medical conditions, drug allergies and previous medical or surgical treatment
- Use of current medications, vitamins, herbal supplements, alcohol, tobacco and drugs
- Discussion of type of anaesthesia (under sedation or general anaesthesia)
- Physical examination of the patient
- Photography for preoperative and postoperative evaluation
Preparation for fat grafting
- Get laboratory testing or a medical evaluation
- Adjust your medications if you have certain medical conditions
- Stop smoking and alcohol well in advance of the scheduled date for surgery
- Avoid taking aspirin, anti-inflammatory drugs and herbal supplements before surgery
- Special instructions will be given on the day before and after surgery
The risks and safety information on fat grafting
It is essential for patients to understand that every surgical procedure has its complications and downtime. However, if a patient is appropriately assessed before the surgery and postoperative care is given adequately, these risks can be eliminated or reduced.
Some of the common risks of fat grafting:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Skin discolouration or bruises at the fat harvested and injected areas
- Swelling
- Temporary numbness or changes in the skin sensation at the face
- Injury to the underlying structures such as blood vessels, muscles or nerves
- Inadequate volume due to fat resorption
- Asymmetry
- Possibility of touch up procedure later
- Anaesthesia risks
Postoperative expectations
There will be minimal swelling, bruises or discomfort at the fat harvested or injected sites for several days that can be controlled with oral medications. Recovery time is usually two weeks after the procedure. Oral antibiotics will be prescribed to reduce the risks of infection.
Postoperative care
- Gentle cold compression is employed for the first 72 hours postoperatively
- A light touch is encouraged to stimulate lymphatic drainage
- Deep massage should be avoided in the first week after fat grafting because an intense directed pressure could displace the fat and force it into an undesirable area
How much will a fat grafting surgery cost?
Cost is always a consideration in elective surgery. The cost of fat grafting can vary widely.
The cost of fat grafting may include:
- Surgeon’s fee
- Hospital or surgical facility costs
- Anaesthesia fees
- Prescriptions for medication, and
- Medical tests
Fat grafting is a cosmetic surgical procedure, and most of the health insurance companies do not cover cosmetic surgeries or their complications.
